In an era where everything is linked to the internet, cybercrime has taken a new and concerning turn with the advent of Ransomware as a Service (RaaS). This approach has made it simpler than ever for attackers to conduct ransomware attacks without requiring sophisticated technological knowledge. RaaS is turning hacking into a business by giving ransomware tools on a subscription basis, with implications that affect organisations all over the globe.
According to current statistics, 5,414 ransomware assaults were recorded worldwide in 2024, representing an 11% rise over the previous year. With ransom demands now averaging USD 5.2 million, the financial effect on firms is enormous. But what exactly is RaaS, and why is it so important? Let us break it down.
What is Ransomware as a Service (RaaS)?
Anyone who lacks technical knowledge can now purchase strong ransomware through a service that functions to target victims. That’s exactly how Ransomware as a Service works. The service operates as a valid Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platform with developers creating tools that users buy for payment or by sharing ransom money.
Here’s how it works:

- Developers: Developers create and support ransomware programs through their hacking knowledge. They provide uninterrupted maintenance alongside technical help, which ensures their ransomware stays useful while avoiding detection.
- Affiliates: The attack execution falls under affiliates since they perform them. The ransomware becomes available after the affiliate pays either through a subscription plan or a ransomware payment. Then, after payment, the developers give affiliates easy-to-use platforms that allow individuals who lack technical knowledge to execute successful attacks.
- Victims: The ransomware delivers harm to business entities and government departments, as well as private individuals who become its targets. When ransomware reaches their computer systems, it silently encrypts vital files until their access is blocked. Attackers request payments that function as ransom to recover the data access code following encryption.
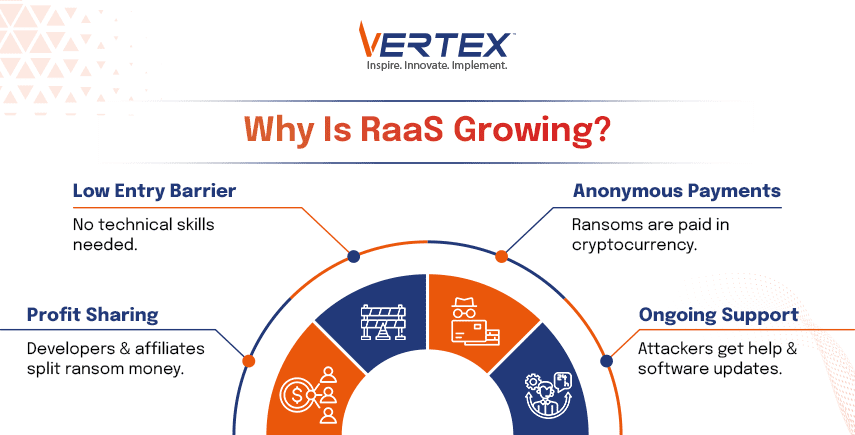
Why Is RaaS So Appealing to Cybercriminals?
Ransomware as a service represents a strong lure for criminal activity because of these particular reasons:
- Low Entry Barrier: RaaS eliminates the need for any previous hacker knowledge to enter the criminal world. The dark web, combined with a small financial investment, enables any person to join ransomware affiliate programs.
- Profit Sharing Models: Developers participating in profit sharing models split the revenue generated from all ransom payments, which yields successful results. Affiliates who work with RaaS do not need initial payments because they simply split the profits with developers.
- Anonymity: The attackers remain difficult to track by law enforcement because victims usually pay with cryptocurrencies that provide payment anonymity.
- Continuous Support: RRaaS platforms combine continuous support services with platform updates, which provides their affiliates with both attack optimisation features and ransom negotiation assistance.
Real-World Example: The Medusa Ransomware
The notorious RaaS implementation exists in the form of the Medusa ransomware. The RaaS malware strategy infected 300 businesses, mainly from the healthcare, education and technology sectors, when it debuted in 2021. The harmful aspect of Medusa ransomware occurs because it launches phishing attacks followed by exploiting unsecured software to gain system access.
The main problem that hinders Medusa’s elimination stems from its ability to operate through native system tools. The ransomware operates undetected by security defenses through the system’s existing standard tools.

The Broader Implications of RaaS
The development of Ransomware as a Service creates consequences that extend further than financial losses. There exist three important issues which need immediate attention.
- Economic Damage: Organizations suffer economic destruction because of ransom payments, along with the substantial costs they need to recover operations. Small businesses typically suffer fatal consequences from this attack.
- National Security Threats: The critical national infrastructure facing attack includes power grids, hospitals and transportation systems, which create substantial hazards to public safety.
- Insurance Challenges: Ransomware incidents continue to grow, so insurance providers charge exorbitant rates for coverage and maintain strict policy conditions.
Combating the RaaS Threat
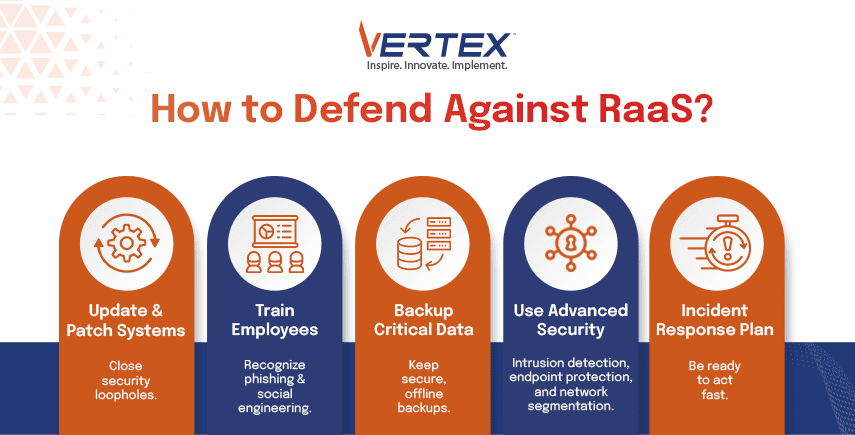
Organisations should implement defences against RaaS attacks. Here are some best practices:
- Enhanced Cyber Hygiene: Systems need regular updates with necessary system patches to shut down security holes. Your organization should establish both powerful password rules and the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Employee Training: The training of employees involves teaching them to recognize both phishing attempts and social engineering tactics. Organizations need to create awareness about unauthorized access because it stands as their main line of defense.
- Incident Response Plans: A documented incident response plan must exist, together with regular testing and preparedness to handle fast reactions during attacks.
- Regular Backups: Maintain secure and isolated backups of critical data. The backup prevents system downtime because you can restore operations before paying ransoms.
- Threat Intelligence Sharing: Your company must join forces with law enforcement departments and industry alliances to stay updated about potential ransomware threats.
- Advanced Security Solutions: This includes using intrusion detection systems together with endpoint protection to detect and stop ransomware in its initial spread.
- Network Segmentation: Your network should be split up into various sections through Network Segmentation to minimize ransomware damage during potential attacks.
Final Thoughts
Ransomware as a Service has established itself as an active criminal network which creates substantial danger for enterprises and public institutions. The increasing sophistication of RaaS platforms requires businesses to establish proactive defensive cybersecurity measures for staying secure.
Knowing RaaS operation methods allows businesses to deploy secure systems which minimize security risks and defend their valuable assets from unauthorized access. Recognizing the imperative for robust cybersecurity defenses, VertexCS offers comprehensive solutions designed to counteract the evolving dangers posed by RaaS.
The core team at VertexCS dedicates itself to asset protection services designed to combat the new security risks of RaaS. They provide complete security solutions starting with advanced threat detection through robust protection frameworks.





