Kiran Boligarla
May 05, 2025Multi-Cloud vs. Hybrid Cloud: Debunking the Myths and Finding Your Best Fit
Cloud computing is transforming businesses with its speed, reliability, and efficiency compared to traditional methods.
But the big question is: which cloud model should you choose?
The multi-cloud model and the hybrid cloud model both offer unique benefits, depending on the needs of your organization.
Your choice can greatly impact the results you expect from your business.
The smart approach is to first understand what each model offers and then align that with your organization’s goals and workflow.
The model that best fits your needs is the right one for you.
In this article, you’ll learn how multi-cloud and hybrid cloud models function and operate.
Plus, we’ll debunk some common myths surrounding them.
This guide will help you make an informed decision about the best cloud model for your organization.
What is Multi-Cloud?
Multi-cloud is when you do not rely on one single cloud vendor for all your needs.
Instead, you distribute your applications and data across multiple clouds.
You can use one or more private clouds, public clouds, or a combination of both.
You are free to choose.
This approach is best for running more applications without adding complexities.
The multi-cloud model also works great with DevOps development and other cloud native technologies.
Key Characteristics of Multi-Cloud
- Vendor Diversity: You can choose from multiple public and private cloud service providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
- Best-of-Breed Approach: You get to choose which vendor you want to work with, depending on their specific cloud services and how they align with your strengths and capabilities. You will not have to be tied down to one specific vendor.
- Flexibility and Choice: When you work with only one vendor, you face issues with cost, interoperability, and data. This is avoided when you opt for the multi-cloud model. You never have to worry about locking in a vendor; you can choose different vendors according to your business needs.
What is Hybrid Cloud?
A Hybrid cloud is a mix of computing environments(on-premises), private clouds, and public cloud services.
This approach is widely adopted because no one relies solely on one public cloud in today’s world.
Also, hybrid cloud services allow you to migrate and manage workloads on different cloud environments, allowing for a setup based on the business needs.
Key Characteristics: Hybrid Cloud
- Integrated Environment: Hybrid clouds combine public and private cloud resources so that they can work together seamlessly.
- Workload Portability: Hybrid cloud offers you the advantage of moving your workloads between different cloud environments based on the specific requirements of the workload.
- Scalability and Control: You get the best of both worlds, offering the scalability of the public cloud with the control and security of a private cloud.
Multi-Cloud vs. Hybrid Cloud: Key Differences
While both multi-cloud and hybrid cloud offer flexibility and scalability, they differ significantly in their architecture and use cases.
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences: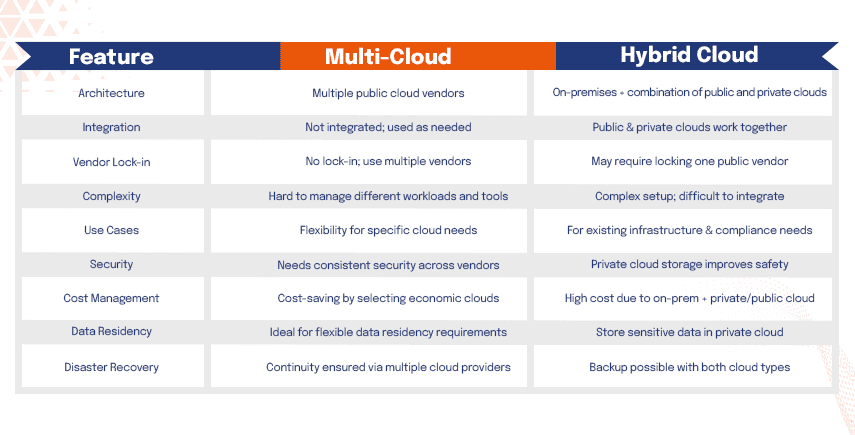
Multi-Cloud vs. Hybrid Cloud: Finding Your Best Fit
Both cloud infrastructures are different, and we have learned about their traits and how we can implement them.
Now, we will deep-dive into the key differences between both.
Multi-model offers the best of multiple public clouds for you to use and scale your organisation.
Whereas the hybrid cloud integrates the public and private clouds for better workload portability.
The multi-cloud model is independent of vendor reliability, and the hybrid cloud is great at using the on-premise infrastructure.
Benefits:
- Multi-Cloud: You get a flexible infrastructure, zero vendor dependency, better cost optimisation, and performance enhancement with the help of workload placement. You also get better reliability during a data loss or attack.
- Hybrid Cloud: You get the best scalability when peak demands hit. You get cost efficiency due to the use of both public and private resources, and you also get better security since there are private clouds to back up your data along with regulatory compliance and low latency for critical applications.
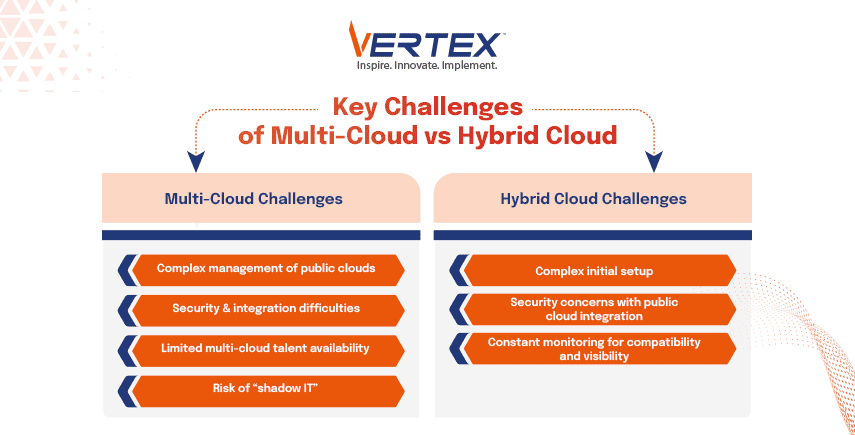
Challenges for Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud
Multi-Cloud:
- Management across different public clouds becomes a bit tough.
- Since there are multiple clouds and workloads, their security and integration are another major complication.
- The availability of people with multi-cloud skills is scarce, and there is also the risk of unmanaged “shadow IT.”
Hybrid Cloud:
- The setup and management of the initial cloud models are complex, and when you counter in the on-premises infrastructure, it gets even more tricky.
- There are security concerns regarding the public cloud integration with the rest of the infrastructure.
- You also have to monitor the data and application compatibility around the clock and make sure that there is enough visibility.
Use Cases:
- Multi-Cloud: If your organisation prioritizes vendor choice and believes in using specific cloud strengths, then you can use multi-model infrastructure. You can also use it for global application deployment for low latency and better disaster recovery across multiple providers.
- Hybrid Cloud: This can be best utilized where data residency requirements are major, along with modernizing applications, all the while retaining their legacy systems. You can also use a hybrid model for handling temporary demand spikes and for enabling DevOps workflows.
Key Statistical Insights:
- The global cloud market is projected to exceed $1 trillion by 2028, as stated by the precedence research.
- According to a report by Spacelift, over 92% of organizations have adopted multi-cloud, and 80% use multiple public clouds; 60% use multiple private clouds.
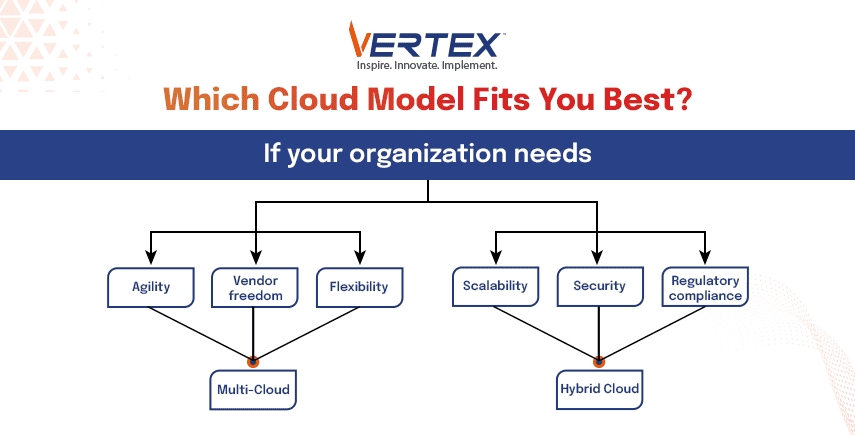
Finding Your Best Fit
The best fit is determined by the needs of your organisation.
Your organisation needs to decide which models suit it the best.
To make a decision, consider your existing infrastructure, security, cost, and desired scalability.
Then factor that in with the things you have learned about both the cloud interfaces.
For example, multi-cloud offers agility and independence, and the hybrid cloud offers scalability and better security.
Conclusion
Both the multi-cloud and the hybrid cloud are powerful cloud deployment models, with distinctive advantages and use cases.
You get flexibility, cost effectiveness, and no vendor lock-ins on a multi-cloud model, whereas on the hybrid one, you get a balance between scalability and control.
In this article, we have discussed the key factors and use cases along with their respective limitations.
So before making the choice for your organisation carefully asses the bussinees needs and consider all the factors we have discussed in this article.
Choosing the right cloud system will result in better agility, optimised costs, and even an edge in today’s cutthroat market.
Recent Blogs
19 May, 2025

19 May, 2025
12 May, 2025

5 May, 2025

28 April, 2025

21 April, 2025

14 April, 2025

7 April, 2025
Recent News

2 February, 2025

14 November, 2024

4 November, 2024

1 August, 2024

6 March, 2024

28 February, 2024

12 June, 2023



