Modern manufacturing is far superior and advanced than its predecessors; the sheer amount of efficiency and agility is far greater. This is all thanks to modern machinery and devices. The factory floor has a changed dynamic thanks to the Internet of Things (IoT), or simply put, the increasing number of smart devices, such as sensors, monitoring machines, and robots, used to automate mundane repetitive tasks. These machines yield a ton of data that can be used to revolutionize operations. However, data in its raw form is useless, we can only use it once it is processed into actionable insights. This is where we use Azure Synapse Analytics, which is a data analytics service provided by Microsoft.
Azure offers a platform where we can analyze and integrate all IoT data in real-time, and with this, we can step into the era of intelligent manufacturing. In this article, we will talk about Azure Synapse and how we can integrate it into our manufacturing. We will also talk about the real-time data flow architecture and analytics within Synapse. We will also cover all the challenges and considerations that are involved in this transformative journey.
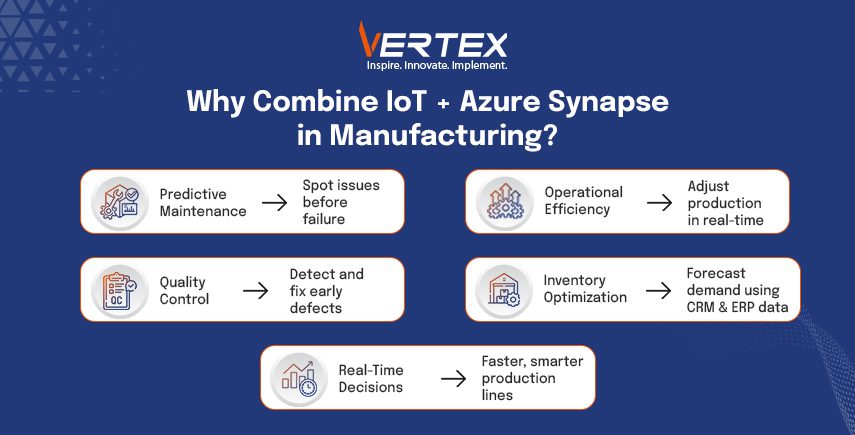
Benefits of Integrating IoT Data with Azure Synapse
The interaction between IoT data and Azure Synapse Analytics will unlock several benefits for the manufacturing organisations. The primary shift is from reactive to predictive maintenance. To put it into simpler terms, with the sensor’s real-time data on machine performance, manufacturers can identify anomalies and predict breakdowns or even small errors before they occur. This is predictive maintenance, which saves precious downtime and optimizes our maintenance schedule. Operational efficiency also benefits from real-time monitoring of production lines. This allows manufacturers to do immediate adjustments to optimize production, reduce waste, and improve overall equipment effectiveness(OEE).
Integrating IoT data with Synapse results in better quality control. When we analyse the sensor data in real-time, it helps us identify the defects and anomalies at an early stage. Then the manufacturers can take corrective actions and minimize the production of faulty goods. This not only saves precious downtime but also results in a better-quality product and less scrap material. Synapse Analytics also takes care of your business data as well, once you have combined the IoT data with other enterprise data sources. Data sources like ERP and CRM ensure accurate demand forecasting and optimized inventory management. The ability to do all these calculations and generate results in real-time is what makes the difference in the manufacturing business.
Key Azure Services for IoT Data Integration
Azure offers such services that make the integration of Synapse seamless, not only this, you can process and store IoT data. Azure acts as a hub that is responsible for communication between the IoT devices and the cloud. This message hub is secure and is meant for two-way communication. This hub is able to handle huge volumes of data from different devices and also ensures safe device management. When data arrives from the IoT hub, Azure Stream Analytics processes it in real-time. This makes sure of the processing, filtering, aggregation, and enrichment of data streams before they land in the Synapse for further analysis.
Azure Event Hubs offers an ingestion service that can handle millions of events per second. This makes it suitable for high-throughput IoT scenarios. If long-term storage for raw and processed IoT data is what you want to do, you can use Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2. This is more cost-effective and also works seamlessly with Synapse. When you combine these services together, you get a scalable IoT data integration with Azure Synapse.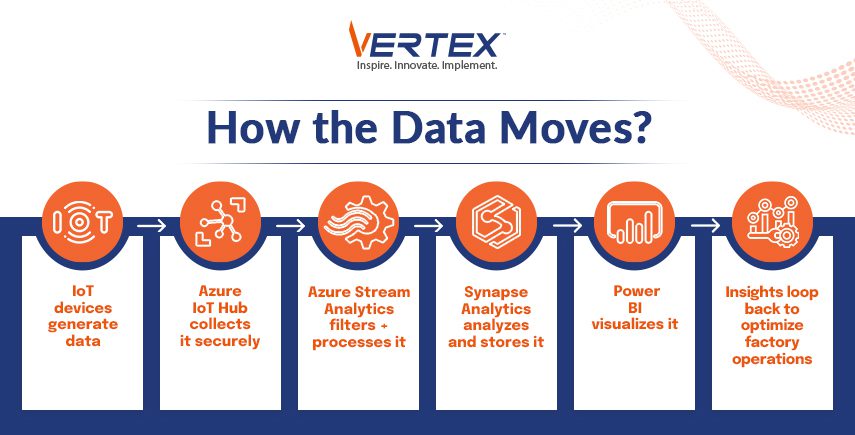
Real-Time Data Flow Architecture
There are several key stages in a real-time data flow architecture for integrating IoT data with Azure Synapse. The data originates from the factory floor through various IoT devices and is then securely transferred to Azure IoT Hub. Then, the data is processed using Azure Stream Analytics in real-time. Operations are then performed, such as filtering signal data points over windows and detecting anomalies based on predefined rules or different machine learning models.
The processed and refined data is then fed to Azure Synapse Analytics, where it is converted into real-time dashboards and insights. The data is also used for SQL pool for performing analytical workloads. Data is kept in Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 for more thorough historical analysis and machine learning tasks. The stored data is accessible to the Synapse Spark pool, which uses this data for large-scale data processing and machine learning model training.Since Power BI is integrated with synapse it can be used to visualize real-time and historical data for making dashboards and reports. These can greatly benefit the stakeholders by helping them mark actionable items based on this data, and then these changes can be directed to the factory floor.
Data Modeling and Analytics in Synapse
Effective data modeling is necessary for optimizing query performance and conducting a meaningful analysis of IoT data. Time series data is a crucial characteristic of the IoT streams, as temperature is taken every ten minutes, as time is crucial in this. Similarly, instead of putting a lot of related data into different tables, we can put relatable data into a single table, which can be useful when we need to find answers. Example – if we put temperature, time, and machine ID in a single table, then we can easily answer the question regarding the reading temperature of that machine in the past hour.
If you are looking for more advanced analytics, then Synapse Spark also provides a powerful environment for running machine learning algorithms on the historical IoT data, which is stored in the data lake. This is then used in the development of predictive maintenance models, anomaly detection systems, and optimized control algorithms.
Use Cases and Success Stories
We have already learned how combining IoT data with Azure Synapse Analytics delivers great results for various manufacturing organizations worldwide. With predictive maintenance, companies have been able to avoid a lot of unplanned downtime and maintenance costs. There is also the benefit of real-time monitoring of production lines, which allows the manufacturer to identify and clear bottlenecks immediately, resulting in increased throughput and reduced waste.
When we use quality control alongside real-time analysis of sensor data, it minimizes the production of defective goods, leading to improved customer satisfaction and reduced scrap waste.
Security and Compliance
The interconnected world of IoT and cloud analytics is all about compliance and security. Azure Synapse Analytics and the associated Azure IoT services make sure there are security features at every layer, and the data in transit is secured through industry-standard encryption. Even in Synapse, Azure Active Directory provides identity and access management, allowing for granular control over who can access and process data. Azure’s comprehensive compliance certifications ensure adherence to industry-specific regulations.
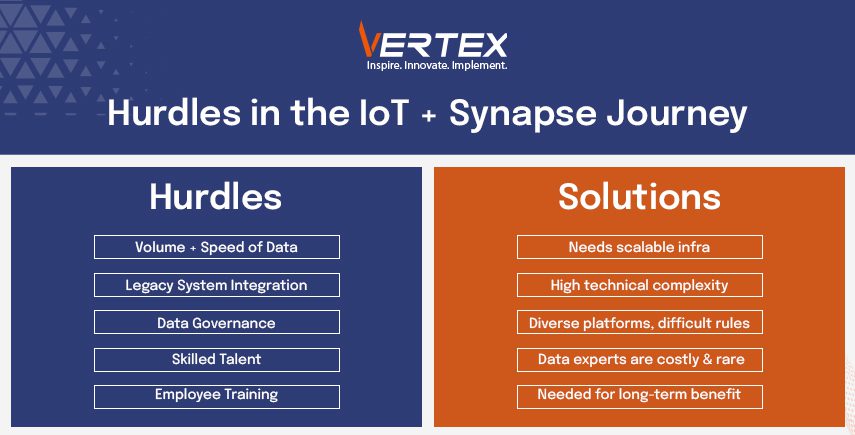
Challenges and Considerations
Though we can agree that integrating IoT data with Azure Synapse is positively fruitful, we can not ignore the challenges that are associated with the process. The sheer volume and the speed of the data require a stable and scalable architecture. There is the issue of integrating old manufacturing systems with cloud platforms, which have a lot of technical hurdles, and governing the data across different IoT platforms can be very complex.
To build and maintain the data pipelines, you need data science and engineering experts, and they are tough to source and are an expensive resource. Organisations also need to train their employees so that they can understand the system and navigate through the system efficiently. If this is followed, then it is beneficial for the organisation in a long run.
Furthermore, to build and maintain the data pipelines, we need data science and engineering expertise, which is tough to come by. Organisations also need to train their employees and make them familiar in the process of navigating these systems efficiently.
By embracing the power of IoT data and the analytical capabilities of the Azure Synapse, manufacturing organizations can profit a lot. Their overall efficiency, agility, and intelligence will rise and start the new era of operational excellence.