Terms like “business intelligence” (BI) and “data analytics” (DA) abound in today’s data-driven corporate scene. Where do they differ, even if both entail learning from data?
We’ll investigate business intelligence and data analytics in this blog, investigating their unique qualities, uses, and features.
Knowing these differences will enable companies to decide which strategy best fits their situation.
What is Business Intelligence?
Business intelligence, or BI, is about turning your data into valuable insights to guide choices.
BI helps companies make data-driven decisions that result in improved outcomes rather than depending on gut emotions or presumptions.
BI is turning challenging datasets into aesthetically pleasing and easily consumed forms, including dashboards, charts, and reports.
These visual aids help companies to grasp why and what is happening in their operations.
Example:
Imagine yourself owning a worldwide online retailer of fashion goods. You wish to monitor monthly sales and find the sources of those increases. BI tools let you create a report showing your monthly sales patterns.
Monthly sales trends:
This report shows a notable increase in sales. The BI tool clarifies “what” is happening—increasing sales. But by looking at the source of the sales trends, you can better understand “why” they’re growing.
Monthly sales from source:
Examining this information reveals that your email marketing has been relatively successful, which helps explain the rise in sales.
Here, BI closes the distance between raw data and valuable insights by integrating data, reporting, visualization, and analysis.
Business intelligence allows businesses to:
- Track performance against standards and goals using data visualization and analysis. For instance, you can track monthly sales, orders, and earnings.
- Discover trends and patterns in big data using BI, fostering a better knowledge of consumer behavior and corporate performance.
- Comprehensive reports and clear visualizations enable corporate leaders to make data-driven choices. Knowing that email marketing went successfully from the above, you can maximize and give them more attention.
By using data to drive proactive decisions, BI helps companies to keep ahead.
Though BI shines in descriptive analysis and reporting, it lags in predictive and prescriptive analytics—where data analytics is most beneficial.
What is data analytics?
Data analytics is the application of computer techniques, machine learning algorithms, and statistical analysis to derive insightful data information.
There are four primary forms to classify data analytics:
- Summarizing and visualizing past data, descriptive analytics helps one to grasp “what has happened.” It pays especially attention to prior performance, trends, and patterns.
- By spotting the underlying causes of trends and patterns, diagnostic analytics helps one to grasp “why something happened”.
- Predictive analytics addresses the “what will likely happen” issue by using statistical methods and past data to project future results.
- Prescriptive analytics addresses “what should we do” and provides advice on reaching particular objectives, guiding companies in their decisions.
Example:
Using our e-commerce example, BI found more revenues from recent email marketing. Data analytics lets you now address “how” such initiatives are performed.
For instance, the success could be due to:
- Customizing emails by audience segmentation.
- Including appealing offers, client comments, and quotes.
Future performance can also be projected with data analytics.
Analyzing past data will help you forecast sales trends for the following several months, enabling you to make preemptive decisions, including inventory building or increased marketing activity, should sales decline.
Comparing business intelligence and data analytics
Comparing data analytics and business intelligence helps one see the overlap and differences between the two areas.
Both fields make use of statistics to derive understanding and backup for decisions. Still, they have various uses and appeal for different company departments.
Here’s a detailed table of the key differences between business intelligence and data analytics:
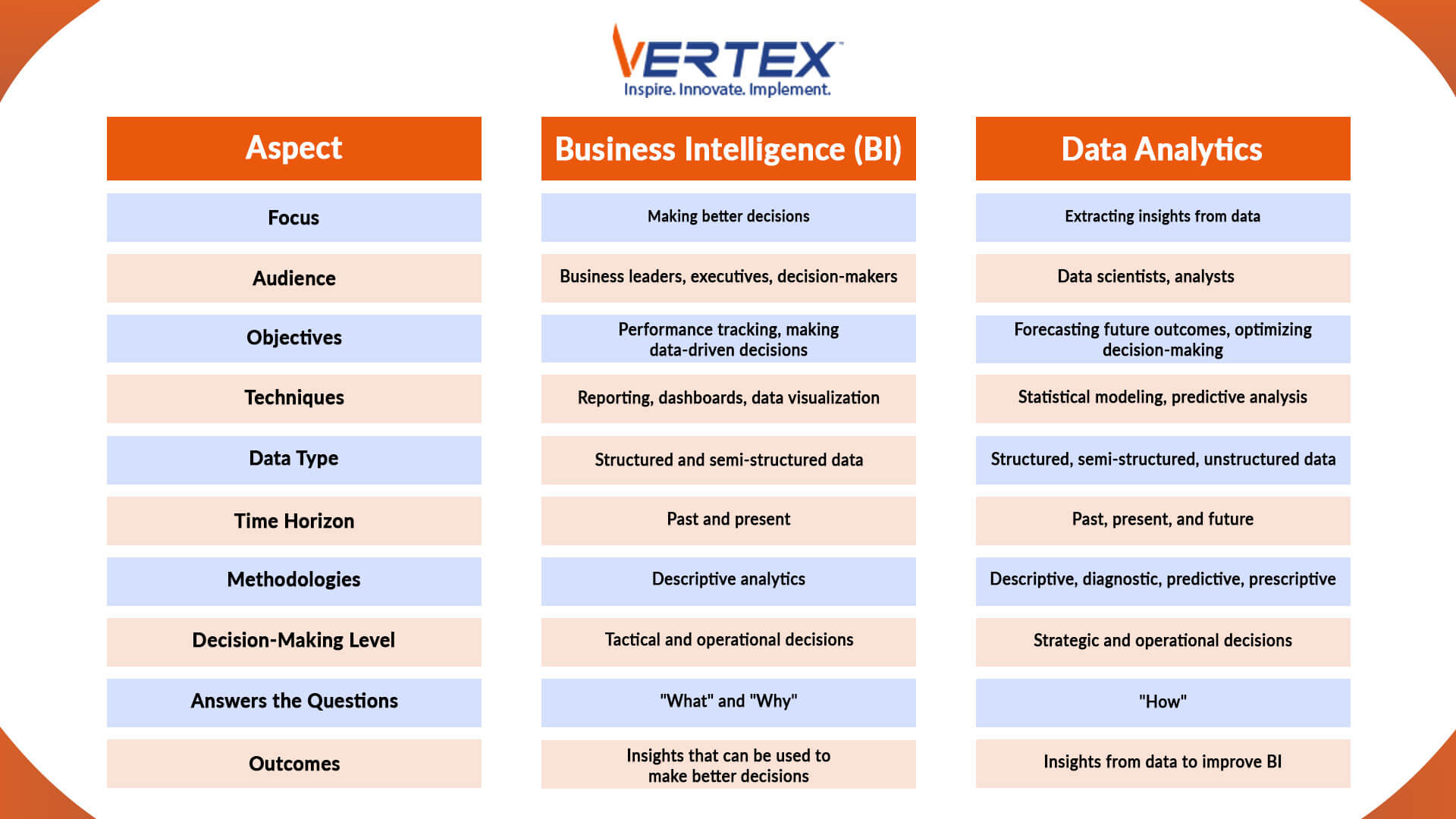
Understanding these differences can help you determine which approach aligns best with your business goals.
Which one for your business: BI or data analytics?
Your company’s needs, goals, resources, and skill requirements will determine whether business intelligence or data analytics best fits you.
- Business intelligence could be the best option if your primary concern is measuring and observing performance using well-organized, consistent data.
- Data analytics would be more appropriate; however, if you manage significant volumes of unstructured data, predictive modeling and advanced analysis—are needed for strategic decision-making.
However, BI and data analytics are not mutually exclusive, and this should be remembered. Many companies use a hybrid strategy, combining data analytics and BI to satisfy their particular needs.
But you could wonder—will using a hybrid strategy require considerable time and financial outlay? In reality, it’s not necessary.
Modern top-rated data analytics products combining BI and data analytics features let you advance your data-driven path without breaking.
Wrapping Up
Data analytics and business intelligence are essential in the changing terrain of data-driven decision-making.
Data analytics provides deeper insights into future outcomes and prescriptive actions, whereas BI shines in clearly, visually comprehending past and present performance.
The proper strategy for your company will rely on your particular objectives and requirements.
Whether your inclination is towards BI, data analytics, or both, the secret is appropriately using your data to propel company success.




